Feeling lost in a sea of numbers? Math problems got you feeling like you’re chasing butterflies in a hurricane? Don’t worry! There’s a secret weapon waiting to be unleashed: the number line. This magical tool isn’t just for elementary schoolers; it’s a powerful ally for anyone who wants to conquer calculations and unlock the secrets of the number system. This article will guide you through everything you need to know about them, from the basics to more advanced applications.
What is a Number Line?
Imagine a ruler, but instead of inches or centimeters, it’s marked with numbers. That’s essentially a number line. In simple terms, it is defined as a straight, horizontal line that visually represents numbers in order, extending infinitely in both directions. It includes both positive and negative numbers, with zero typically positioned at the center. Points on the line are marked at equal intervals to represent integers, fractions, and decimals. Think of it as a magic road map that helps us navigate the world of numbers.
Here is the visual representation of what it looks like:
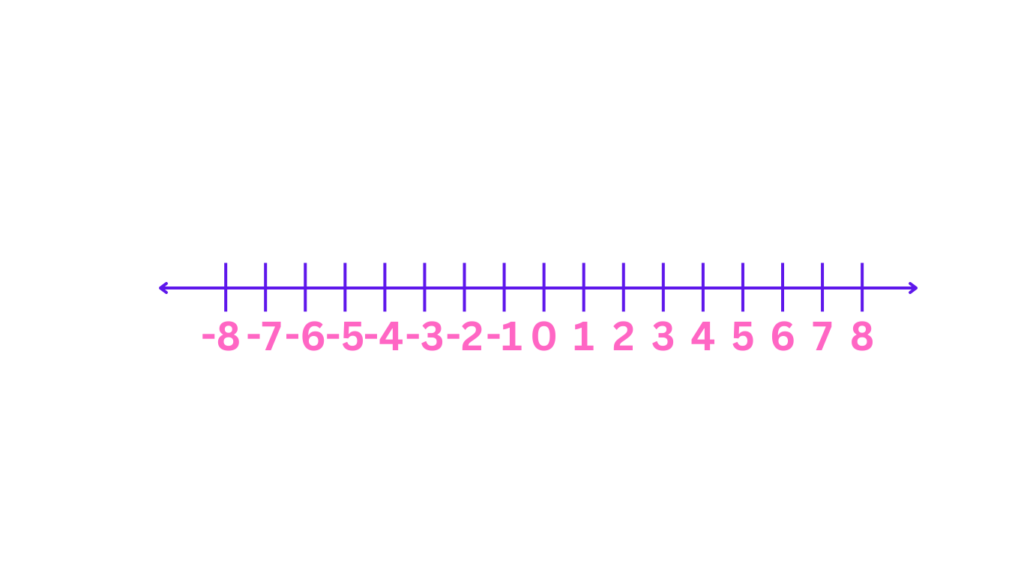
Imagine a straight line with small marks at regular intervals. At the center is zero. Numbers to the right of zero are positive, and numbers to the left are negative. Each mark represents a number, and the distance between each mark is equal, providing a clear visual representation of numerical order.
Basic Components
Now, let’s delve deeper into the basic components of this mathematical marvel:
-
Zero Zone: Look closely at the center of the number line. You’ll find zero, the grand marshal of the number world. It acts as a dividing line, separating positive numbers (to the right) from their negative counterparts (to the left). Positive numbers are like happy campers, getting bigger as they move to the right. Negative numbers, well, they’re a bit more like grumpy gremlins, getting smaller as they march to the left.
-
Equal Intervals: Here’s the magic trick: the distance between each number on the line is always the same. This consistency is what makes the number line so powerful. It allows us to easily compare the size of numbers – the further a number is to the right, the bigger it is, and vice versa.
-
Positive and Negative Numbers: Remember those positive and negative characters we mentioned? The number line gives them a place to shine. Positive numbers (like 1, 2, 3) represent quantities greater than zero. Negative numbers (like -1, -2, -3) represent quantities less than zero. Think of a temperature gauge – positive numbers represent warmth, while negative numbers represent coolness.
How to Draw a Number Line
Drawing a number line is simple and straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Start with a Straight Line: Use a ruler to draw a horizontal line on a piece of paper.
- Mark the Center: Place a mark at the center of the line and label it as zero (0).
- Create Equal Intervals: From the center, mark equal intervals to the right for positive numbers and to the left for negative numbers.
- Label the Points: Write the corresponding numbers above or below each mark.
Tips for Accuracy
- Use a Ruler: Ensure the line is straight.
- Consistent Spacing: Keep intervals equal to avoid confusion.
- Clear Labels: Write numbers neatly to ensure readability.
Using a Number Line for Basic Operations
Number lines are incredibly useful for basic arithmetic operations. Let’s explore how they work for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Addition and Subtraction
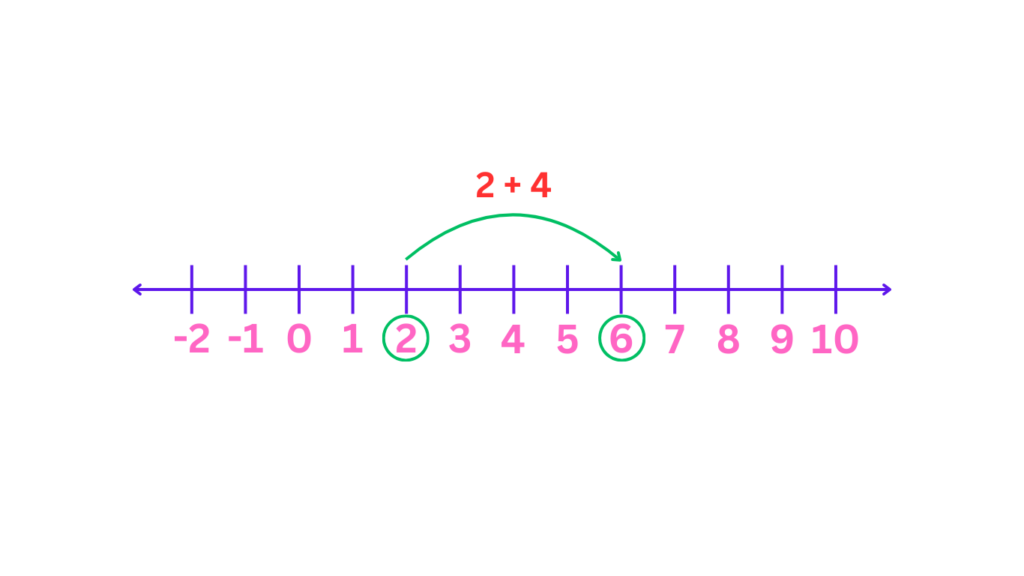
Addition: To add numbers, start at the point representing the first number. Move to the right the number of spaces equal to the second number. The point you land on represents the sum. For example, to add: 2 + 4, start with 2 in the number line and move 4 spaces to the right from 2. The number we land in is 6, and this is the number that we get when we add 2 + 4.
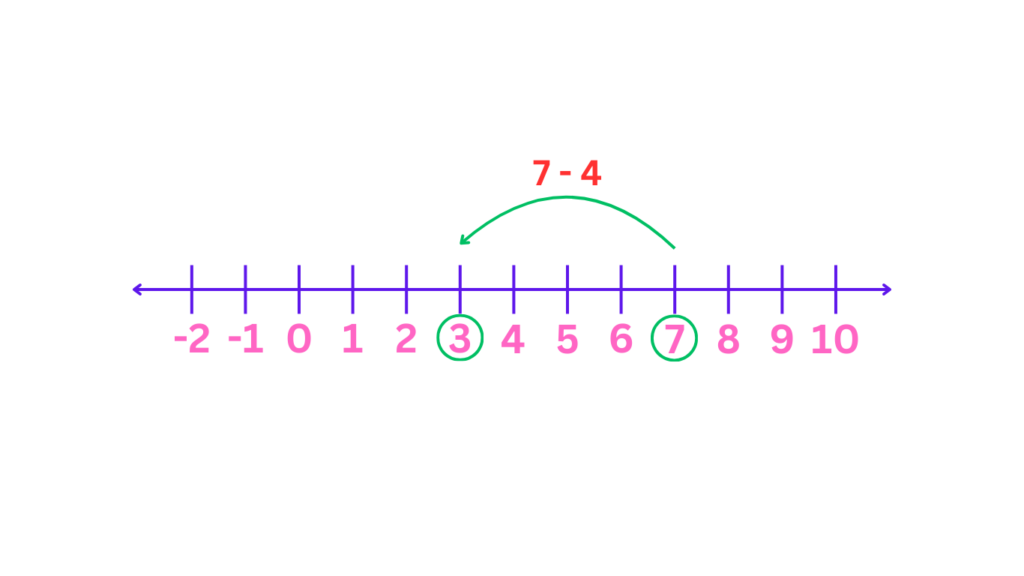
Subtraction: For subtraction, start at the point representing the first number. Move to the left the number of spaces equal to the second number. The point you land on represents the difference. For example, to subtract: 7 – 4, start at 7 and move 4 spaces to the left from it. The number we land in is 3, and this is the number that we get when we subtract 7 – 4.
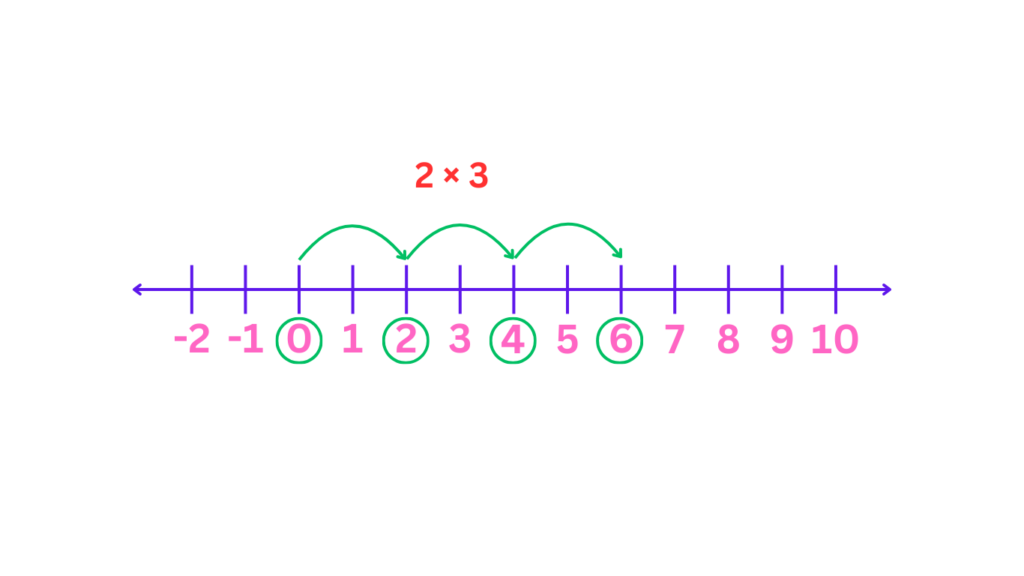
Multiplication and Division
Multiplication: Use the concept of repeated addition. For example, to multiply 2 by 3, start at 0, move two steps right to 2, then again move 2 two steps right to, and finally 2 steps right to 6. The point you land on (6) is the product.
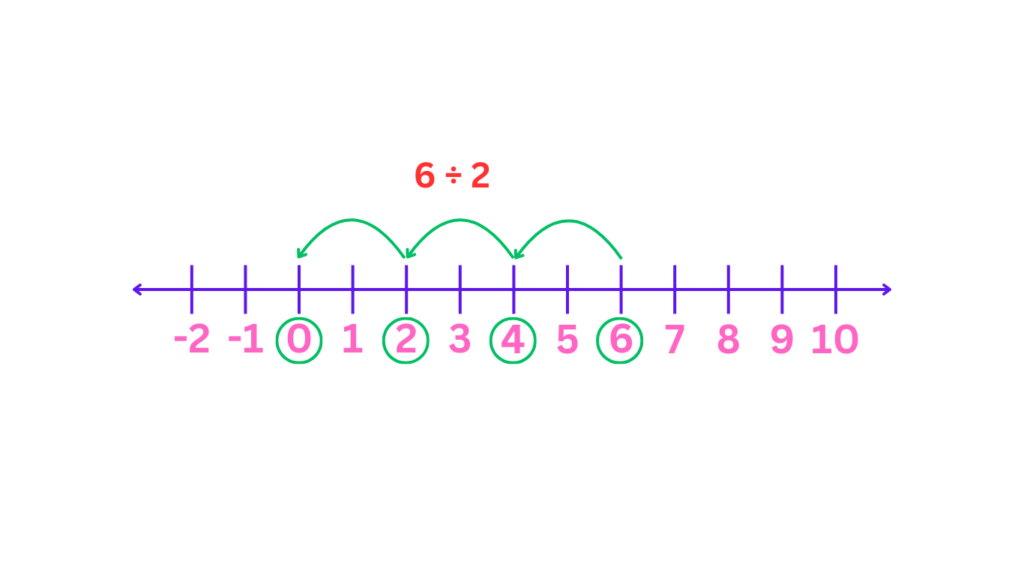
Division: Think of it as repeated subtraction. To divide 6 by 2, start at 6 and move the left 2 spaces repeatedly until you reach zero. Count the steps to find the quotient (3).
Advanced Uses of Number Lines
Number lines are not just for basic math; they are also essential for more complex concepts like fractions, decimals, and negative numbers.
Fractions and Decimals
Fractions: To represent fractions, divide the intervals between whole numbers into equal parts. For example, to plot 1/2, find the midpoint between 0 and 1.
Decimals: Similar to fractions, place decimals by dividing intervals. For example, 0.5 would be halfway between 0 and 1.
Comparing and Ordering: Number lines make it easy to compare and order fractions and decimals. Simply plot the numbers and see their relative positions.
Negative Numbers
Understanding and plotting negative numbers on a number line is straightforward. They are placed to the left of zero, with the same spacing as positive numbers.
Real-life Examples: Negative numbers are used in various real-life contexts, such as temperatures below zero, financial debts, and elevations below sea level.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
While using number lines is generally straightforward, there are common mistakes that can occur. Here’s how to avoid them:
- Misplacing Points
Ensure that points are accurately placed by using consistent intervals. Double-check your marks before labeling them.
- Incorrect Intervals
Keep intervals equal to maintain the integrity of the number line. Using a ruler or graph paper can help achieve this.
- Direction Confusion
Remember that moving to the right indicates positive movement (addition), and moving to the left indicates negative movement (subtraction). Clarify this concept to avoid confusion.
Conclusion
In summary, number lines are a powerful tool in mathematics, providing clarity and simplicity for understanding various concepts. From basic arithmetic to complex fractions and negative numbers, it is your go-to visual aid. By mastering its use, you can enhance your math skills and tackle mathematical problems with confidence. So, grab a ruler, draw your number line, and start exploring the endless possibilities it offers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a number line?
A number line is a visual representation of numbers in order, extending infinitely in both directions, with equal intervals between points.
How do you use a number line for addition and subtraction?
In addition, move to the right from the starting point. In subtraction, move to the left. The point you land on represents the result.
Can a number line be used for multiplication and division?
Yes, multiplication can be viewed as repeated addition and division as repeated subtraction on a number line.