Did you know that the very screen you’re reading this on is made up of thousands of tiny polygons? Yes, those seemingly simple shapes are everywhere, from the honeycombs of bees to the towering skyscrapers in our cities. But what is a polygon, really? In this article, we’re going to unlock the secrets of these amazing geometric shapes, taking you through everything you need to know. So, buckle up and get ready to learn everything about what is a polygon and become a polygon pro.
What is a Polygon?
So, what is a polygon? Simply put, a polygon is a flat, two-dimensional shape with straight sides that are fully closed. This means that a polygon’s sides connect at their endpoints, forming a closed loop. The word “polygon” comes from the Greek words “poly,” meaning many, and “gon,” meaning angle. Therefore, polygons are shapes with many angles.
Properties of Polygons
Understanding the properties of polygons is essential for identifying and working with these shapes. Here are some key properties to consider:
Sides and Vertices
A polygon is defined by its sides and vertices. The sides are the straight edges that form the shape, and the vertices are the points where two sides meet. For instance, a triangle has three sides and three vertices, while a hexagon has six sides and six vertices.
Angles
Polygons have both interior and exterior angles. The sum of the interior angles of a polygon can be calculated using the formula:
Sum of interior angles = (n – 2) x
where n is the number of sides. For example, a quadrilateral (four-sided polygon) has a sum of interior angles equal to:
(4−2) × 180 degree = 360 degree
The exterior angles of a polygon always sum up to 360 degrees, regardless of the number of sides.
Diagonals
A diagonal is a line segment connecting two non-adjacent vertices of a polygon. The number of diagonals in a polygon can be calculated using the formula:
Number of diagonals = n(n – 3) /
where n is the number of sides, for example, a pentagon (five-sided polygon) has:
5 (5-3) / 2 = 5 diagonals
Types of Polygons
Now that we know what is a polygon, let’s dive into the various types of polygons you might encounter. Polygons can be categorized in several ways based on their characteristics.
Regular Polygons
Regular polygons have all sides and angles equal. Think of an equilateral triangle or a square—these shapes have uniform sides and angles, making them symmetrical and aesthetically pleasing. Regular polygons are often used in design and architecture due to their balance and harmony.
Irregular Polygons
In contrast, irregular polygons have sides and angles that are not all the same. These shapes lack the symmetry of regular polygons but are just as important. An example of an irregular polygon is a scalene triangle, where all sides and angles are different.
Convex vs. Concave Polygons
Polygons can also be classified as convex or concave. A convex polygon has no interior angle greater than 180 degrees, and its vertices all point outward. In contrast, a concave polygon has at least one interior angle greater than 180 degrees, and it may have some vertices pointing inward. Think of a star-shaped figure as an example of a concave polygon.
Simple vs. Complex Polygons
Simple polygons do not intersect themselves—they have a straightforward, single boundary. A complex polygon, on the other hand, intersects itself and creates more intricate shapes. An example of a complex polygon is a star with intersecting sides.
Classifying Polygons by Number of Sides
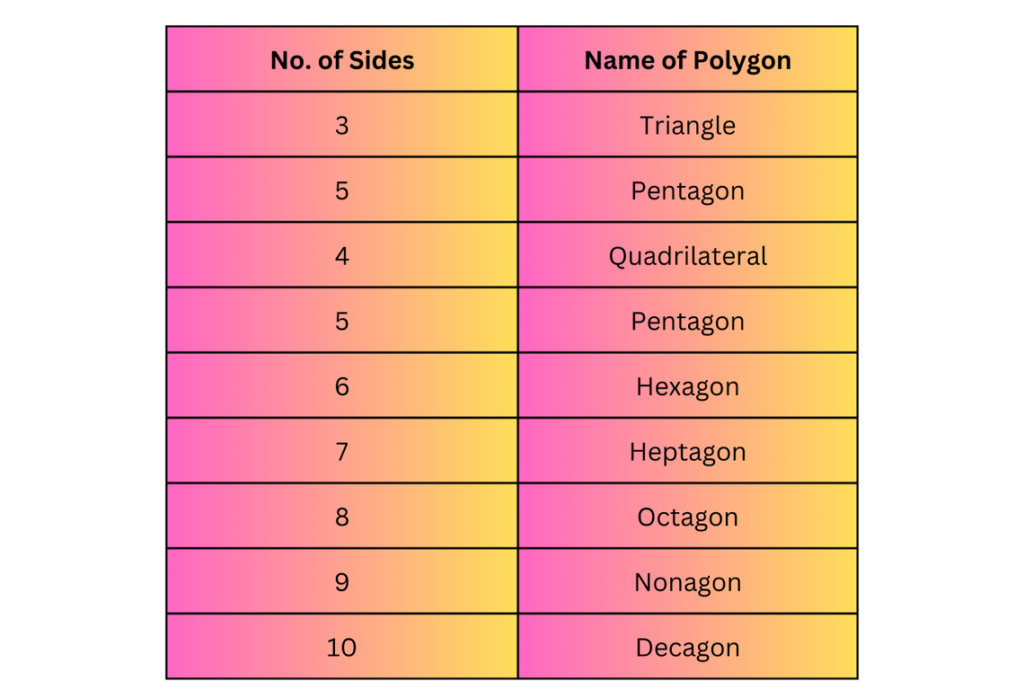
Polygons are often classified by the number of sides they have. Let’s look at some common polygons and their characteristics:
Triangles (3 sides)
Triangles are the simplest type of polygon, with three sides and three angles. They come in various forms:
- Equilateral triangle: All sides and angles are equal.
- Isosceles triangle: Two sides and two angles are equal.
- Scalene triangle: All sides and angles are different.
Quadrilaterals (4 sides)
Quadrilaterals have four sides and four angles. They include:
- Square: All sides and angles are equal.
- Rectangle: Opposite sides are equal, and all angles are 90 degrees.
- Rhombus: All sides are equal, but angles are not necessarily 90 degrees.
- Trapezoid: Only one pair of opposite sides is parallel.
Pentagons (5 sides)
Pentagons have five sides and five angles. A regular pentagon has equal sides and angles, while an irregular pentagon does not.
Hexagons (6 sides)
Hexagons have six sides and six angles. They can be regular (all sides and angles equal) or irregular. The regular hexagon is particularly notable for its natural occurrence in honeycombs.
Heptagons (7 sides)
Heptagons have seven sides and seven angles. Regular heptagons have equal sides and angles, while irregular heptagons do not.
Octagons (8 sides)
Octagons have eight sides and eight angles. The most famous octagon is the stop sign. Regular octagons have all sides and angles equal.
Nonagons (9 sides)
Nonagons have nine sides and nine angles. Like other polygons, they can be regular (all sides and angles equal) or irregular.
Decagons (10 sides)
Decagons have ten sides and ten angles. Regular decagons are less common in everyday life but are used in various mathematical contexts. Irregular decagons do not have all sides and angles equal.
Real-Life Applications of Polygons
At this point, we have learned most of the things about what is a polygon and its types, but you must have the question of why we should learn all these, from what is a polygon, and its properties, to its classification. Polygons are not just theoretical shapes; they have numerous real-life applications. Here are some areas where polygons play a crucial role:
- Architecture
Architects use polygons extensively in building design. From the rectangular layout of rooms to the triangular support structures, polygons provide stability and aesthetic appeal. Modern architecture often features complex polygons for innovative and eye-catching designs.
- Nature
Polygons are abundant in nature. For example, the hexagonal cells in a honeycomb maximize space and structural efficiency. The natural world often uses polygonal shapes for efficiency and functionality.
- Art and Design
Artists and designers utilize polygons to create intricate patterns and designs. Whether it’s in graphic design, textile patterns, or digital art, polygons offer a versatile and visually appealing element.
Fun Facts and Trivia About Polygons
Polygons have some interesting historical facts and unique properties that make them even more fascinating:
- The concept of polygons dates back to ancient Greece, where mathematicians like Euclid studied their properties.
- The name for a 12-sided polygon is a dodecagon, and a 20-sided polygon is called an icosagon.
- The world’s largest polygon structure is the Great Pyramid of Giza, with its square base.
How to Draw a Polygon
Drawing polygons can be a fun and educational activity. Here’s a step-by-step guide to drawing a simple polygon, such as a hexagon:
- Tools Needed: Gather a ruler, a compass, and a pencil.
- Draw the Center Point: Start by marking the center point of your polygon.
- Set the Compass: Adjust the compass to the desired radius of your polygon.
- Draw a Circle: Using the center point, draw a circle. This circle will help ensure that all sides of your polygon are equal.
- Mark the Vertices: Divide the circumference of the circle into equal parts (for a hexagon, divide it into six parts).
- Connect the Dots: Use the ruler to connect the points around the circle. Voila, you have a hexagon!
Common Problems and Solutions
When working with polygons, you might encounter some common problems. Here are a few tips to help you avoid and solve these issues:
Common Mistakes
- Incorrect Angle Calculation: Always double-check your calculations, especially for interior and exterior angles.
- Unequal Sides in Regular Polygons: Use precise tools like a compass and ruler to ensure all sides are equal.
Tips and Tricks
- Practice Drawing: The more you practice drawing polygons, the better you’ll get.
- Use Technology: Tools like graphing software can help create perfect polygons.
Conclusion
Polygons are more than just simple geometric shapes; they are fundamental elements of both natural and human-made structures. From the hexagonal cells in a honeycomb to the intricate designs in architecture and art, polygons are everywhere. Understanding what is a polygon and its properties can help you appreciate the complexity and beauty of the world around us. Whether you’re a student, a designer, or just a curious reader, we hope this article has unlocked the secrets of these amazing geometric shapes for you. So, go ahead and explore the fascinating world of polygons.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a polygon?
A polygon is a flat, two-dimensional shape with straight sides that are fully closed. It is formed by connecting a series of straight line segments to form a closed loop.
How are polygons different from other shapes?
Polygons are distinguished by their straight sides and closed structure. Unlike circles or curves, polygons are made up of line segments.
What are the most common types of polygons?
The most common types of polygons include triangles (3 sides), quadrilaterals (4 sides), pentagons (5 sides), and hexagons (6 sides).
Can polygons be three-dimensional?
No, polygons are strictly two-dimensional shapes. However, polygons can be used as faces of three-dimensional solids, such as cubes and pyramids.